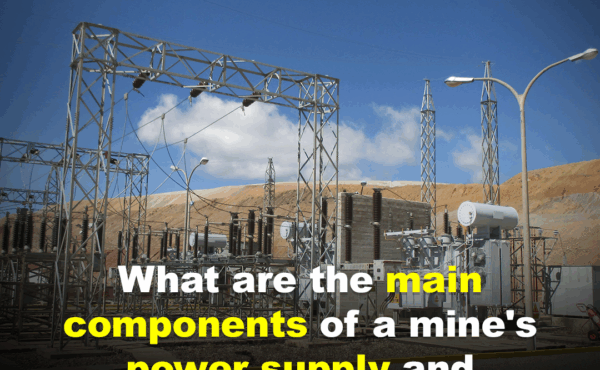
A mine’s power supply and electrical system are critical for its operations, encompassing a comprehensive network designed to deliver reliable and efficient power to various equipment and processes. The main components typically include:
- Total Step-Down Substation (High Voltage Distribution Station): This is the initial point where external high-voltage power (e.g., 220-110kV) is transformed down to the mine’s high-voltage distribution level (e.g., 35-10kV). It supplies power to various substations and transformers within the mine area.
- High-Voltage Distribution Lines: These lines transmit the high-voltage power from the main substation to different areas of the mine, including workshop substations and other major electrical equipment.
- Workshop Substations: These substations further reduce the voltage (e.g., from 35-10kV to 380/220V) to supply power to specific operational areas and equipment, such as mining machinery.
- Transformers: Essential static electrical devices that use electromagnetic induction to step up or step-down AC voltage to the required levels for various components throughout the system.
- High-Voltage Switchgear: This equipment manages and controls the flow of high-voltage power. It comprises components such as vacuum circuit breakers, isolating switches, relay protection devices, grounding switches, voltage transformers, and current transformers.
- Low-Voltage Distribution Lines: These lines distribute the lower voltage power from workshop substations to individual machines and equipment within the plant area.
- Low-Voltage Switchgear and Circuit Breakers: These components manage and protect the low-voltage distribution, ensuring safe power supply to individual machines and preventing electrical overloads.
- Cables: The fundamental structure for transmitting electrical current, consisting of conductors, insulating layers, and protective layers to ensure safe and efficient power delivery (ZeusBTC, n.d.).
This robust electrical infrastructure is crucial for the continuous operation of mining equipment, contributing to cost-effective energy consumption and reduced environmental impact, particularly in electrically powered systems like In-Pit Crushing and Conveying (IPCC) (Mohammadi et al., 2023).
Ever wondered how massive mines get the power to run all their machines? Share your thoughts!